Italy has been in focus recently for several reasons: the dramatic human impact of the early outbreak of COVID-19, the equally dramatic social and fiscal policy measures taken by its government in response to the economic impairment and, finally, the wild swings in its bond prices. In this blog entry, we review recent macro and policy developments in Italy. Part 2 will focus on our related investment strategy.
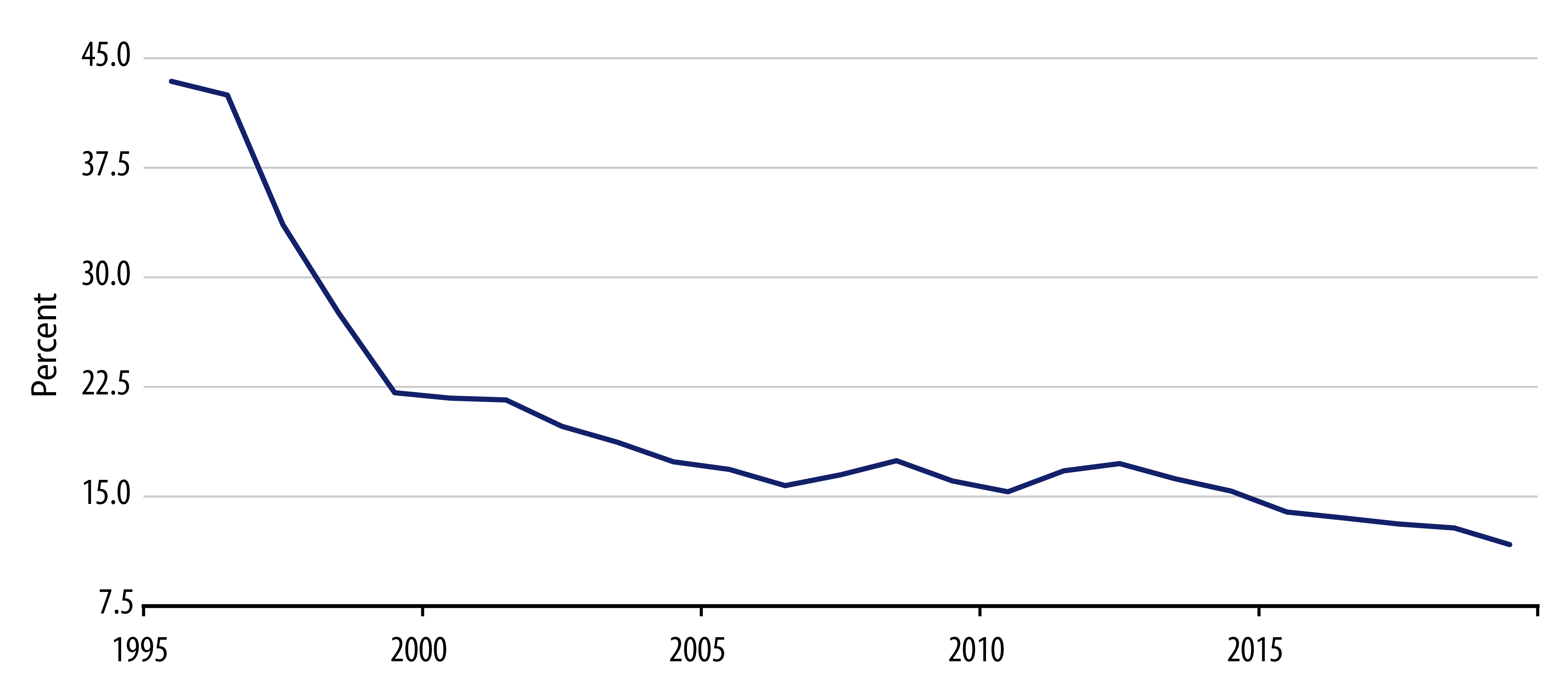
At a national level, the pandemic-induced lockdown has led to a significant drop in output but also in demand, similar to what has been experienced in other European economies. The latest data indicate that the Italian economy shrunk by almost 5% in the first quarter, with worse news to come in Q2. The Italian government currently estimates that its economy will contract around 8% this year, and sees a fiscal deficit of around 10%. By comparison, the IMF’s most recent forecast is somewhat more negative on growth but a bit more sanguine regarding the deficit; however, this assessment does not take into account Italy’s fiscal stimulus worth around 3% of GDP. Both sides agree that Italy’s debt-to-GDP level will rise by around 20 percentage points this year and approach 160%. While this well-known fiscal vulnerability is certainly reason for concern for market participants as well as rating agencies, it is worth highlighting that alternative measures that better reflect Italy’s ability to pay for debt service would indicate a lower level of concern, as long as the sovereign’s borrowing cost remains low (Exhibit 1).
At the EU level, Italy has played a vocal role in policy discussions, arguing vehemently for joint and several borrowing by European sovereigns, an effort the market dubbed “coronabonds”. Ultimately, the support package adopted by the European Council of Heads of State or Government did not include that type of financing source and it is unlikely that the recovery fund, currently still being designed, will include it. Yet, Italy could still be a major beneficiary of all elements of this package: the backstop for the existing short-term work scheme (cassa integrazione), lending to corporates by the European Investment Bank (EIB) and, politically somewhat more difficult, borrowing from the European Stability Mechanism (ESM). While accessing the ESM facility makes financial sense for Italy—after all, it is going to be much cheaper than borrowing in the market—the domestic political discussion largely evolves around the “stigma” associated with this type of lending and the perception of conditions associated with this loan. In reality, the conditionality is limited to spending the money on healthcare-related items—and paying back the loan such that the ESM can retain its AAA rating. Meanwhile, the recovery fund is also likely to include a grant element geared at particularly hard-hit regions in Europe, and it is highly likely that Italy would benefit from that.
The European Central Bank (ECB) is also currently working in two major areas to soften the fallout from the coronavirus and ensure monetary transmission in the eurozone is not hampered. The ECB has increased its asset purchases, including the creation of the €750 billion Pandemic Emergency Purchase Program (PEPP). Also, in an attempt to prevent a credit crunch, the ECB had cheapened existing long-term financing facilities, provided additional temporary ones and loosened the eligibility criteria for the collateral pool in repo operations to include “fallen angels”, i.e., debt of issuers that have lost their investment-grade rating after April 7, 2020. While the ECB has so far not increased the size of the PEPP or removed the investment-grade criterion for asset purchases (with the exception of Greece being made eligible for the PEPP but not the other asset purchase programs), these precedents could clearly become relevant if the rating agencies were to push Italy’s ratings closer to below-investment-grade.
To date, Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s have affirmed Italy’s current ratings and outlook at BBB (negative) and BBB- (stable), respectively. DBRS downgraded the trend to “negative” while leaving the rating at BBB (high), still three notches above high-yield territory. Whereas all these assessments took place at the pre-established dates, Fitch took off-cycle action and downgraded Italy to BBB- (with stable outlook) in late April. Fitch’s downgrade (and potential further rating actions) will likely heighten the concern of market participants that one of the largest sovereign debt issuers in the world would fall below investment-grade but it would also invite a policy reaction, including one from the ECB, along the lines mentioned above.
From an investment perspective, the yield spread between 10-year Italian bonds and German bunds of the same maturity has moved from 130 bps in mid-February to almost 280 bps a month later and currently stands at around 230 bps. We believe that ultimately the ECB will be willing to take more measures, including expanding the PEPP program in size but also enabling it to buy sovereign fallen angels. Indeed, the most recent monetary policy statement explicitly noted that “purchases will continue to be conducted in a flexible manner” and “until … [the Governing Council] judges that the coronavirus crisis phase is over”. This is a strong part of the argument supporting our overweight to Italian bonds. Please see Part 2 of this blog in the coming days for more details on our trading strategy.

